Unit 13
Solutions
What is a solution?
A solution is a homogeneous mixture of two or more pure substances — can be solid, liquid, or gas.
In the solution, the solute (comparatively less volume) is dispersed uniformly throughout the solvent (comparatively more volume).
Forming a solution and a chemical reaction may look similar (solvent disappears), but it's only a solution if the solvent can be recovered (such as by evaporation of saltwater, salt can be recovered).
Natural Tendency towards Mixing
Mixing causes more randomness in the position of the molecules, increasing entropy (randomness of the universe), which is favorable).
Intermolecular Forces
In order to determine whether a solution will form, we need to take into account:
- Solute-solute interactions (must be overcome to disperse the particles)
- Solvent-solvent interactions (must be overcome to make room for the solute)
- Solvent-solute interactions (occur as particles mix)
In order for a solution to be formed, its Gibbs Free Energy must be negative, so the process is spontaneous. As a reminder, Gibbs free energy () is given by .
This means that (enthalpy change of creating solution) must be close to the sum of and , so in the above equation is zero or negative. Then, will be negative and the process will be spontaneous.
However, the sum doesn't need to be exactly the same as , since creating a solution increases entropy (), which can compensate for a slightly positive and still produce a negative .
For example, ionic compounds dissolve if attraction between the solvent and ions are strong than the attraction between the ions themselves. Therefore, ionic compounds (such as salt, ), dissolve in water and very polar solvents only.
Molecular compounds dissolve in solvents with similar polarity — polar solutes in polar solvents, nonpolar solutes in nonpolar solvents. As explained above, the values need to be similar.
For example, the more polar a molecule, the better it dissolves in water.
Liquids that mix in all proportions are miscible, while liquids that do not mix in one another are immiscible.
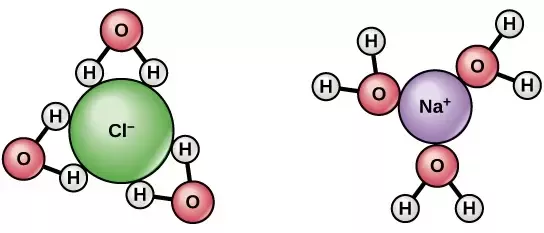
Molecular orientation in solution
If a solution does form (for example with water), remember that the orientation of molecules is based on polarity.
Solubility
Solubility is the maximum amount of solute that can dissolve in a given amount of solvent at a given temperature.
Saturated solutions have the maximum amount of solute dissolved, while unsaturated solutions have less solute dissolved.
Solubility is affected by:
- Solute-solvent interactions
- The stronger the solute-solvent interaction, the greater the solubility of solute in that solvent
- “Like dissolves like”
- These were explained above.
- Pressure (for gaseous solutes)
- The solubility of solids and liquids is not affected by pressure
- Gas solubility increases when pressure increases
- Temperature
- For most solids, as temperature increases, so does solubility. This is due to Gibbs free energy (explained above), since increased temperature = increased entropy
- For all gases, as temperature increases, solubility decreases. This is because increased temperature = particles moving faster = higher chance of gas particles escaping the solvent
- Cold rivers have higher oxygen content than warm rivers. This is why fish die in rivers when factories along the banks of the river use the water to cool down equipment, and then return the warm water to the river.
Supersaturated solutions
A supersaturated solution is a solution that holds more solute than is normally possible at that temperature.
These are formed by increasing temperature, saturating the liquid, and then decreasing the temperature slowly. If the solution doesn't contain disturbances to crystallize around (dust, bumps in the glass of the container, etc.), the solute cannot crystalize back out.
Units of Concentration
Molarity
Molarity is the most important unit of concentration, and is defined as:
Molality
Molality is defined as:
Differences between molarity and molality
With solutions where water is the solvent, molarity and molality are similar (since 1 mL is about 1 gram, so 1 L is about 1 kilogram).
Molarity varies with temperature, since volume changes. Molality does not, since mass stays the same.
Chromatography
Chromatography is a technique that involves separating substances based on the differences in polarities.
Often, dots of the substance are placed on a plate coated in silica gel (which is very polar). Then, the plate is immersed in a nonpolar solvent. The more the substances move up with the nonpolar solvent, the more nonpolar they are. If the substances stay closed to the start (bottom) of the plate, they are adhering to the polar plate, and are therefore more polar.
Since distance travelled by the substance depends on the distance traveled by the solvent, we compare the retention factor, , between different plates.
Colligative Properties
Vapor pressure lowering
Solutions have a lower vapor pressure than solutions, since additional attraction to the solute prevents solvent molecules from escaping and contributing to vapor pressure.
Boiling point elevation
Boiling takes place when vapor pressure is equal to atmospheric pressure. Due to vapor-pressure lowering, if a solution has more solute dissolved in it, the temperature must be raised higher before boiling can occur.
Freezing point depression
Solute in water prevents molecules from crystalizing and lowers the freezing point. This is how anti-freeze works, by adding extra particles to the liquid so the liquid can't crystalize and freeze.